Mathchem Python package for matemathical chemistry calculations
Mathchem is a free open source Python package for calculating topological indices and other invariants of molecular graphs.
Downloads
Mathchem for Sage
mathchem-1.1.3.spkg
Mathchem for Python
mathchem-1.1.3.zip
Sources
Git-hub: https://github.com/hamster3d/mathchem-package
Python Package Index: http://pypi.python.org/pypi/mathchem
Features
Together with Sage or SciPy it can be used in QSAR/QSPR research. The package allows to read various molecular file formats, retreive data from online NCI database using search query, import graph structure from Sage and NetworkX graphs structures or parse a g6 string.
Input fromats
- SD file (.sdf)
- Sybyl 2 Molfile (.mol, .ml2, .mol2)
- MDL Molfile (.mol)
- Graph6 (.g6)
- Sparse6 (.s6)
- Planar code
- NCI database direct queries
Calculations
-
Common graph properties
Order, Size, Diameter, Degree of all vertices, Eccentricity, Connectedness -
Matrices
Adjacency matrix, Incidence matrix, Laplacian matrix, Signless Laplacian matrix, Normalized Laplacian matrix, Distance matrix, Resistance Distance matrix, Reciprocal Distance matrix, -
Graph spectra
Spectrum of the all matrices above, Spectral moments, Spectral radius, Energy, Incidence Energy Topological indices
Zagreb M1 Index, Zagreb M2 Index, Connectivity index (R), Eccentric Connectivity Index, Randic Index, Atom-Bond Connectivity Index (ABC), Estrada Index (EE) for all matrices, Distance Estrada Index (DEE), Distance Degree (DD), Reverse Distance Degree (rDD), (Schultz) Molecular Topological Index (MTI), Distance Sum, Balaban J index , Sum-Balaban Index, Kirchhoff Index (Kf) or Resistance, Wiener Index (W), Terminal Wiener Index (TW), Reverse Wiener Index (RW), Hyper-Wiener Index (WW), Harary Index (H), Sum-Connectivity Index, Geometric-Arithmetic Index, Multiplicative Sum Zagreb Index, Multiplicative P1 Zagreb Index, Multiplicative P2 Zagreb Index, 148 Discrete Adriatic Indices
Installation
Mathchem can be installed as a normal Python module or(and) as a Sage module.
Sage is a free open-source mathematics software system licensed under the GPL. It combines the power of many existing open-source packages into a common Python-based interface. Its mission is to create a viable free open source alternative to Magma, Maple, Mathematica and Matlab.
Sage uses Python virtual enviroment which use an isolated instance of Python interpreter. This means that all the packages intalled for system Python are not available in Sage. Thus to use mathchem both in system Python and Sage the package must be installed twice as described below.
Requirements
Mathchem was designed as a lightweight self-contained library. However the package requires that Numpy was installed before. Cirtainly it requires Python interpreter which may be already pre-installed in OS.
As Python module
There are two ways to install mathchem as a Python modeule. Since mathchem is included to Python Package Index, one can use the pip tool. The main advantage of this method is that the package can be easily updated with one line in terminal. First pip checks for dependencies and install them first. Mathchem depends on Numpy the part of SciPy.
pip install mathchem
Another way is to use the module built-in setup.py installer.
- Download python module archive file from the homepage.
- Unpack it and run:
python setup.py install
All these instructions are given for a UNIX-like system. For Windows the process of installation is similar. Since mathchem is a normal Python module, the official Python manual how to install modules can be applied.
As Sage module
- Download spkg file the homepage.
- Save it into your sage directory
-
Run sage with command to install a new package:
sage -f mathchem-1.0.9.spkg
The official instructions on installing additional packages for Sage can be found on the homepage of the project www.sagemath.org
After that you can use mathchem in your sage programs.
Examples
In this section we give several examples of how mathchem can be used in practice.
Import
In the example above we put the Mol class instance into variable m. Here we invoke the class constructor with a graph6 string GhCH?_ which represents a carbon skeleton of 3,4 - Dimethylhexane (C8H18) molecule.
>>> import mathchem as mc
>>> m = mc.Mol('GhCH?_')
Another way to input structure data is to read a file containig molecular data stucture records.
>>> import mathchem as mc
>>> mols = mc.read_from_sdf('compounds.sdf', True)
Here we read a sdf file and allow hydrogens to appear as vertices in molecular graphs by setting the second argument of read_from_sdf method to True. The default value of the argument is False. After executing this code the variable mols will contain a list of all records from the file compounds.sdf.
Integration with Network X
NetworkX is a Python language software package for the creation, manipulation, and study of the structure, dynamics, and functions of complex networks. For further calculations outside of mathchem package the Mol class instance can be easily converted to Network X graph.
>>> import mathchem as mc >>> import networkx as nx >>> m = mc.Mol(’GhCH?_’) >>> g = m.NX_graph() >>> nx.is_bipartite(g) True
Integration with Sage
Sage is a powerfull free open-source mathematics software system which contains more then 100 mathematical packages. We can use the power of Sage together with mathchem. In the following example we convert mathchem molecular graph to Sage Graph, visualize it and check for hamiltonicity.
sage: import mathchem as mc
sage: m = mc.Mol('GhCH?_')
sage: g = m.sage_graph()
sage: g.is_hamiltonian()
False
sage: g.show()
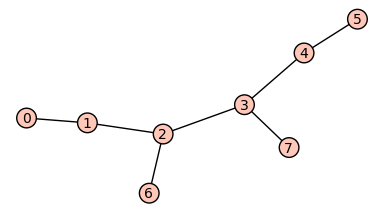
Calculations
First import mathchem
sage: import mathchem as mc
Now we want to import some data. This time we will use NCI database to obtain a test set. Here is an axample how to query all the compounds with NSC number from 1 to 1000:
sage: mols = mc.read_from_NCI_by_NSC('1-1000')
sage: len(mols)
993
The actual number of retreived records is 993. Suppose we are going to have deal with distance matrix and we must be sure that we have only connected graphs for tests. The following code will filter our set. Here we use Python filter function.
sage: mols_c = filter(lambda m: m.is_connected(), mols) sage: len(mols_c) 980
The filter function takes every item of the list mols, checks whether it is connected and if so append this item to a new list mol_c. In the code above we used a lambda-function which allows to create functions on-the-fly. The lambda-functions is the powerful mechanizm of Python allowing to avoid defining a number of small functions and make the code shorter. Now let us do some calcualtions:
sage: bj = [m.balaban_j_index() for m in mols_c]
Now bj list contains calculated Balaban J index for each compound in mol_c.